Governance is the backbone of any professional industry and cloud compliance is its extension. Without it, the entire structure of an organization is at high risk of losing relevant data with the company facing legal action, harming its reputation.
The goals and objectives of a business impact the senior executives, board of directors, employees, and valuable customers. Therefore, it is significant to understand the importance of cloud computing regulations. Ensuring that data is not only secure but also compliant with the changing government rules for the extensive and intersecting web portals.
This article will provide a detailed overview of navigating the vast cloud network by understanding the importance of pivotal frameworks. These regulations guide an organization towards safeguarding their operations and building customer trust.

The convenience of the cloud should never be taken for granted and understanding regulatory standards creates a robust security cover. There are a number of international, federal, and industry-specific rules that a company should research before jumping into cloud services.
These include standard business decrees like
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) for the protection of personal data in the EU, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) for health information in the US, and the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) for payment card transactions.
Maintaining compliance in this terrain often requires the expertise of cloud consultants, who can provide businesses with support in order to implement the solutions decided upon.
THINGS TO CONSIDER
Legal teams aalso play a pivotal role in developing a compliance strategy that addresses everything from data sovereignty issues to industry-specific regulations.
Designing and implementing a best-in-class cloud governance framework is time-consuming but it’s worth every risk that could infiltrate your business. A careful risk assessment and management strategies with the IT and legal team are necessary.
Before migrating data or services to the cloud, a thorough analysis should be conducted to identify potential vulnerabilities. The team should also designate controlled access to specific systems for unnecessary outside intervention.
This step is not a one-time process; it requires constant monitoring as per the changing landscape of threats and compliance requirements. To effectively manage risks, enterprises should implement robust security software, such as encryption and security audits.
By doing so, they add an extra layer of safety but also demonstrate to governing bodies that they are taking proactive steps to follow the required standards.
In an advanced technology era, the threat to privacy and losing valuable data is always pervading. Many companies either fail to focus on vulnerable areas of business or are not willing to invest time in regulatory practices.
The graph below indicates the seriousness of large-scale data breaches over the years. Millions of users were impacted due to cybersecurity issues with well-known companies. The reason to follow strict cloud-based regulations is necessary for every small and big industry.
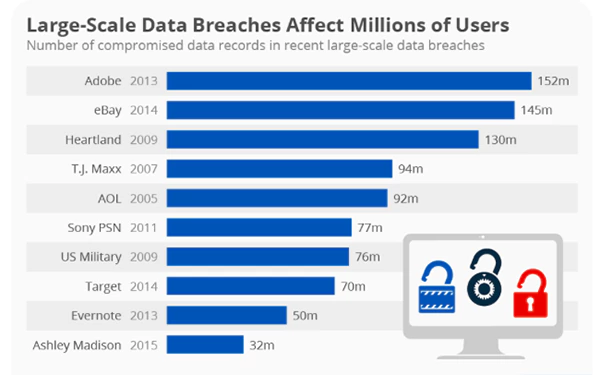
In the coming years as hackers are becoming more invasive, the requirement for advanced software will increase. Apart from that businesses need to be aware of legal rights like GDPR, which not only mandate the protection of personal data but also grant individual rights over their data.
Organizations must ensure that they have clear policies and procedures in place for data handling, retention, and deletion. Moreover, they should empower customers by providing transparent information about how their data is used and by offering tools for data control.
One key aspect to navigating cloud computing regulations is selecting the right cloud service provider (CSP). While a CSP helps an enterprise understand the regulatory landscape with all legal procedures, it also builds a good reputation that stakeholders find worthy of investment.
Many CSPs offer compliance certifications and features that can ease the compliance journey. However, it’s important to remember that while CSPs can provide the tools and environment for compliance, the ultimate responsibility for ensuring compliance rests with the cloud service customer.
Cloud compliance should not be seen as a burden but rather as an opportunity to control the future of an enterprise. It requires continuous monitoring and adaptation to keep pace with evolving regulations, threats, and technological advancements.
Nowadays, it has become easier to implement automated tools for cloud management which provide real-time insights and alerts to companies to take immediate corrective actions. With a team that is trained and experienced, businesses can ensure that the entire organization remains vigilant about compliance practices.
Risk management is an integral part of a cloud governance framework. It is a strategic approach to ensure compliance efforts are aligned with the organization’s broader objectives.
Frameworks such as COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies) can help businesses structure their governance and standard activities by identifying potential risks associated with cloud adoption.
A detailed assessment also extends to developing strategies to mitigate risks but also vendor lock-in risks and regulatory compliance risks. Implementing safety controls, backup and disaster recovery mechanisms and regular vulnerability checks are other facets of proactively managing disruptions.
Compliance with industry regulations and internal policies results is a significant aspect of cloud governance. Navigating the complex world of intersecting networks and preventing loss of data will always be of paramount importance at present and in the future.
It is always best to be prepared for any hurdle that could disrupt the business and have a negative impact on customers. It is the legal and moral responsibility of every enterprise to adhere to the transforming legal and web regulatory requirements.
Investing in a team that manages cloud computing risks and threats with awareness fosters a culture of professional infrastructure that could be trusted by investors and customers alike.